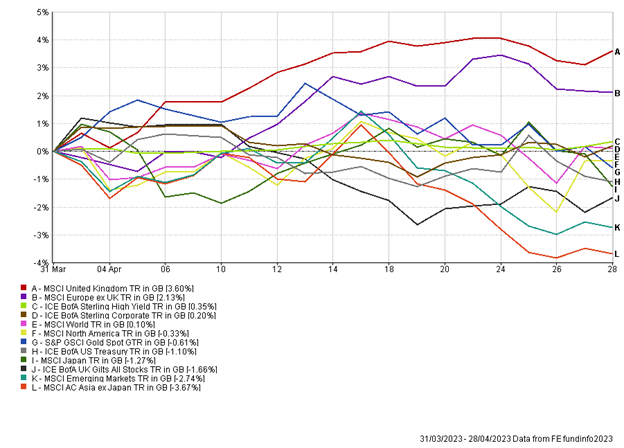
Five weeks ago, we spoke about the luxury brand Moet Hennessey Louis Vuitton (LVMH) becoming the first European brand to achieve the $500bn market cap value. However, the luxury goods market has been hit over the last two weeks. With the rally initially being driven by demand from China there has been a cooldown in sales, with LVMH shares falling -5.55% over the last month, down to a market cap value of $412bn.
House prices in the UK have fallen at their fastest annual pace in 14 years, as Nationwide reported a 3.4% drop in house prices in May. This fall in house prices is the largest (year-on-year) drop since July 2009, which will be welcomed by potential first time buyers, however rising mortgage rates are still a factor in play. With the UK’s inflation rate slowing less than expected to 8.7% and core inflation rising, the Bank of England are still expected to hold rates higher for longer and this in turn will drive up mortgage interest rates. For first time buyers or home owners whose fixed rate terms will be ending soon, a two-year fixed rate mortgage is around 5.49%, significantly greater than the 3.25% it was a year ago.
Wednesday was the last day of May with inflation results for many of European countries released. German inflation fell to 6.1%, its lowest level in over a year, with headline inflation also falling in France, Spain and Italy. With greater than expected falls in price growth, the next ECB meeting on 15th June in Frankfurt will be interesting to watch as investors had hoped for greater caution on further rate hikes. On Thursday, ECB President Christine Lagarde, acknowledged rate hikes are working but as ever maintained a strong tone stating the hiking cycle needs to continue “until we are sufficiently confident inflation is back on track to return to target”, referring to the inflation target of 2%.
Another hot topic this week has been the story of Artificial intelligence (AI). Nvidia are the world’s largest semiconductor company, who seemingly are the biggest winners of the AI boom as on Tuesday they briefly hit the $1trillion market cap mark. Nvidia are responsible for creating around 80% of the chips (graphic processing units) that power AI. Only Apple, Alphabet (Google), Microsoft and Amazon have reached this $1trillion milestone, with Nvidia’s stock value tripling in under eight months reflecting the rush in interest. Despite the sky-high valuations, investors seem to believe Nvidia’s business has room for growth as AI is still in its early stages and has not yet seen mass adoption.
US Non-farm payrolls were released this afternoon, with a staggering 339k jobs added in May beating the market expectation of 190k. This is a rise to April’s revised figure of 294k. With the strong labour market and inflation in the country falling, the expectations of the US falling into a recession dampens, however it may prove that the next US Fed meeting is not the turning point for rates.
Early this week, Turkey’s president Mr Erdogan was re-elected, winning another five years in power in a decision that has split the country. President Erdogan, who has led the country for the last 20 years, secured 52% of votes in a narrow win, the closest the president has come to being unseated. Notoriously known for harsh levels of intimidation and jailing opposition politicians and journalists, the population are torn over the president’s use of state resources and control of media to influence the result. With the dust settling, a spiralling economy, rampant inflation of 43% and significant Syrian migration commotion within the country are tasks the President will have to face immediately.
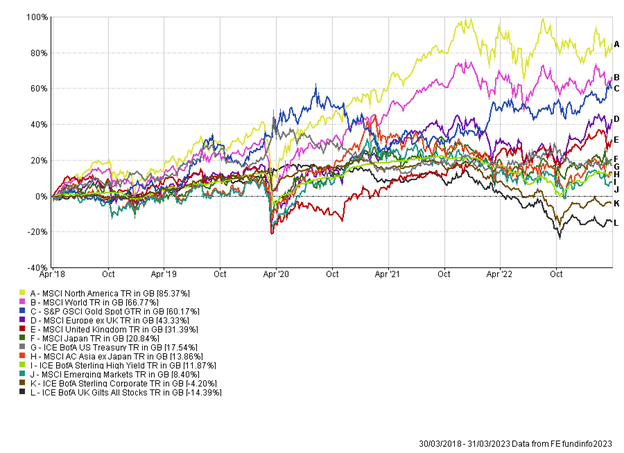
Continued signs of rate hikes, imminent recession fears and political unrest are just some of the issues challenging investors currently. Despite this we continue to focus on long-term opportunities, while ensuring there is sufficient diversification in portfolios to help protect against short term unease. To quote Simon Evan-Cook, who sits on our investment committee, with long-term investing it’s best to “keep your hands in the car at all times”.
Nathan Amaning, Investment Analyst
Risk warning: With investing, your capital is at risk. The value of investments and the income from them can go down as well as up and you may not recover the amount of your initial investment. Certain investments carry a higher degree of risk than others and are, therefore, unsuitable for some investors.