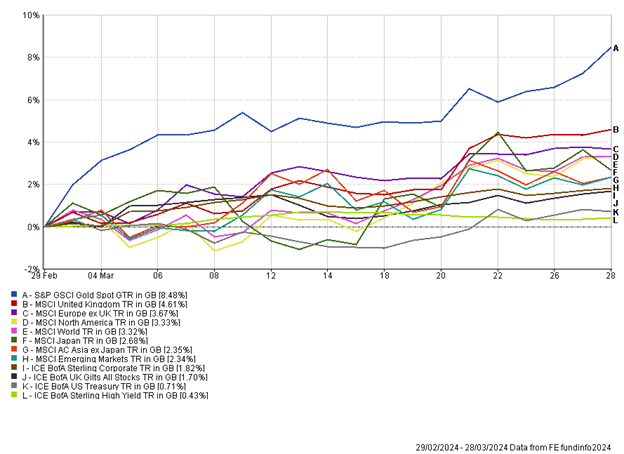
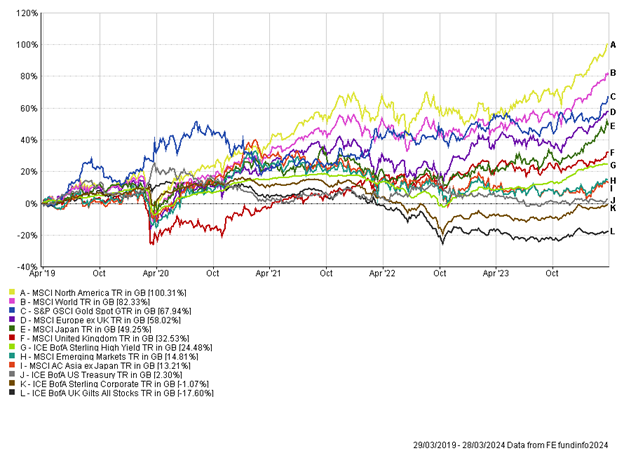
This week we moved into the month of May. The month is often associated with transition and growth, with warmer times approaching for the Northern Hemisphere and nature coming out in full bloom. The first few days of May in markets have certainly been in keeping with growth, after a disappointing April for asset markets.
The US was the main focus this week, with the Fed meeting to set interest rates, alongside key employment data today. As expected, US interest rates were held steady at 5.5%. The US Fed is not yet confident enough that inflation will soon reach target, and as such plan to maintain interest rates in restrictive policy. The shift in market expectations surrounding interest rate cuts in the US has been stark in 2024. Heading into the year the market was pricing in 6-7 interest rate cuts, but the market now only expects one interest rate cut from the US in 2024. The huge shift back towards “higher for longer” rate policy has caused a significant headwind for fixed income assets this year.
UK equities have had a strong two months, with the momentum carrying on this week. At the time of writing the FTSE 100 is on course to close at a new record high. The reflationary narrative has been supportive for sectors such as mining and financials, which are big constituents of the UK index. Persistent mergers and acquisitions (M&A) have also provided a short-term boost for the UK. We’ve recently seen sizeable bids for Anglo American (£31bn) and Darktrace (£5bn) and this week there were rumours that private equity was circling to buy Alpha FMC, a £400m market cap company. The share price surged around 38% on the rumours, and it is pleasing the company was a large position in our UK smaller companies fund. Card Factory, a position in our global value fund, announced strong results this week and re-instated its dividend. The positive news helped lift the share price 7% as the turnaround of the company continues.
UK share buybacks have been a common occurrence in recent months, however, it was one of the biggest companies in the world who announced a huge share buyback program this week. Apple posted mixed Q1 results, with iPhone sales plunging over 10%. However, such is the strength of the balance sheet, the company announced an increase to its small dividend and a £110bn share buyback program. While Apple results delighted markets, Starbucks update left a bitter taste for investors. The coffee company announced a surprise drop in sales in both US and international markets, leading to a 10% drop in share price. With the cost of a cup of coffee increasing, it appears some consumers are now cutting back on consumption.
Switzerland had been the first developed market central bank to break cover and cut interest rates. This week Swiss inflation figures showed inflation reached a four-month high of 1.4% in April (year-on year). The acceleration in inflation was a surprise to markets and may be cause for concern for the Swiss central bank if the trend persists.
US Non-Farm Payroll data showed 175,000 jobs had been added to the economy, much lower than the expected 238,000. February’s jobs data was revised down by 34,000. Average hourly earnings increased less than expected while unemployment made an unexpected jump to 3.9%. Collectively the data, for the first time this year, highlighted a slowing labour market. The bad news appeared to be good news for markets, with equities pushing higher this afternoon, while bond yields fell (prices up) for government bonds. The data will potentially allow the US Fed to ease interest rate policy in the near term.
After a difficult April the start of May has proven to be positive, with both equities and bonds rallying over recent days. Here in the UK, we have seen new all-time highs in the FTSE 100, while M&A activity continues at pace. Government bonds have enjoyed a strong end to the week as weaker US jobs data has once again shifted the interest rate pendulum back in the direction of cuts. We think it is important to be diversified at a portfolio level against the uncertain and changing macroeconomic backdrop.
Andy Triggs, Head of Investments
Risk warning: With investing, your capital is at risk. The value of investments and the income from them can go down as well as up and you may not recover the amount of your initial investment. Certain investments carry a higher degree of risk than others and are, therefore, unsuitable for some investors.