The Month In Markets – September
September was an extremely difficult month for markets, with most asset classes witnessing sharp falls in value. The continuing story around inflation and interest rates was partly to blame, while the UK had additional pressures created by the mini-budget.
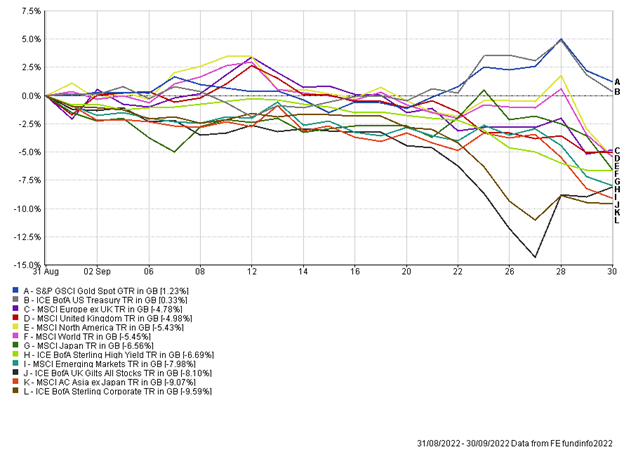
One of the major headwinds for global assets during the month was higher than expected inflation data from the US. This has been a recurring issue for equities and bonds in 2022. Higher inflation leads to investors then pricing in higher interest rates which will be required to combat inflation, and this had negative implications for both equities and bonds.
US headline inflation came in at 8.3% for August, marginally ahead of expectations of 8.1%. However, it was the core month-on-month inflation that really spooked markets. Core inflation strips out highly volatile items such as food and energy and this accelerated by 0.6% month-on-month. This is one of the US Fed’s preferred inflation measures and led markets to immediately price in higher interest rates ahead, with the expectation that the US Fed funds rate would be 4.6% at the end of 2022.
The reaction to the inflation data was felt immediately, with US equities falling over 4%, suffering their worst individual trading day since 2020. We also saw yields on US government bonds rise sharply (prices fall).
Digging a little deeper into the data it was the shelter/rents component that was one of the biggest drivers behind the inflation data. The initial impact of higher interest rates may mean it is harder for first time buyers to get on the property ladder, which could lead to greater demand for rental properties and push rents even higher!
While US inflation data was a headwind for markets, the UK mini budget caused extreme volatility in UK bonds and currency markets. You will notice from the chart that both UK gilts (government bonds) and UK sterling corporate bonds suffered significant drawdowns in the month. These moves are far from normal, and the price action witnessed in UK government bonds has been described as a once-in-a-generation type event.
The mini budget shocked markets with much greater unfunded tax cuts than anticipated. There were two big problems with this – a huge increase in debt issuance and increasing budget deficits made the UK less creditworthy, while the tax cuts could lead to increased consumer spending and higher inflation, and therefore may warrant even higher interest rates. This was enough to send both UK government bonds and Sterling nosediving. Within 24 hours of the mini budget we witnessed sterling hit an all-time low of $1.035 against the USD (it should be noted that from here were have seen something of a mini-recovery in sterling). As the sell-off in government bonds continued, many liability-driven investment (LDI) pension funds ran into trouble. There came a breaking point where the Bank of England had to step in and provide support to the bond market, announcing they would buy an unlimited amount of long-dated UK government bonds for a finite period of time. The news was enough to reverse some of the pain that had been felt and led to a significant relief rally. Sterling corporate bonds were caught up in the mayhem, in part as they derive some of their price from government bond yields, but also because in a scramble for liquidity many LDI schemes became forced sellers of these bonds in order to meet cash calls.
The dramatic rise in government bond yields in the UK caused issues in the mortgage market. On the 27th September almost 300 mortgage deals were pulled from the market, and we have since witnessed a large increase in borrowing costs for homebuyers. Any benefits of the tax cuts for consumers will likely be wiped off in much higher mortgage payments going forward. With a deteriorating outlook for the UK consumer, domestically facing UK equities suffered the brunt of the pain.
Asset-class diversification in September was very limited, with most bond and equity markets falling. One respite came from a weakening sterling, which benefits sterling investors holding foreign assets. Within portfolios we have been increasing exposure to currencies such as the USD this year and that has been a positive contributor.
While undoubtedly difficult at the moment, the price movements we are seeing are creating longer-term opportunities. Within fixed income markets for example, we can now receive yield to maturities in excess of 4% for lending to the UK or US governments, even in shorter-maturity bonds, which typically carry much less interest rate risk. Two years ago, this yield on shorter maturity government bonds was closer to 0%.
Andy Triggs
Head of Investments, Raymond James, Barbican
Appendix
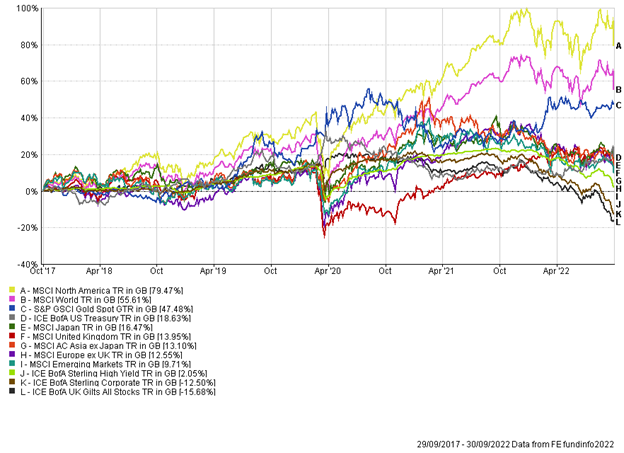
5-year performance chart